1. Basic Principles of Seawater Electrochlorination Technology
Seawater electrochlorination technology uses seawater as raw material and converts chloride ions in seawater into highly oxidizing chlorine - based substances through electrolysis. These substances can efficiently kill microorganisms in water and prevent them from breeding in the cooling system of nuclear power plants.
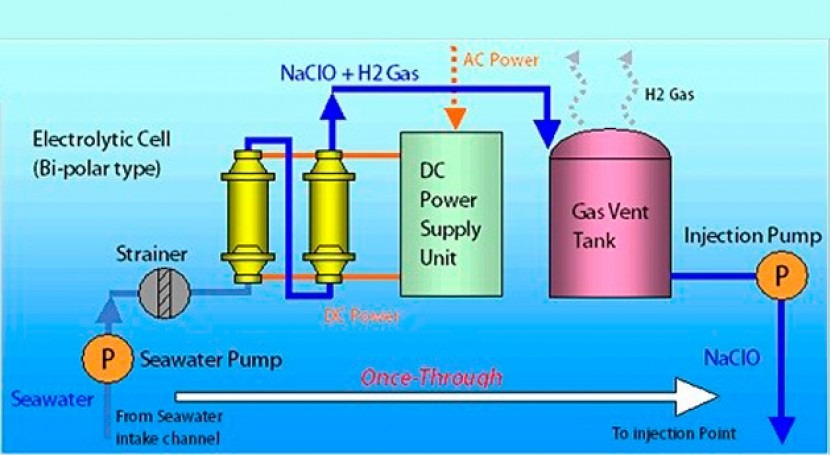
During electrolysis, seawater passes through the electrolytic cell and undergoes chemical reactions under the action of electrodes. Oxidation reaction occurs at the anode, where chloride ions lose electrons to generate chlorine gas; reduction reaction occurs at the cathode, where water molecules gain electrons to generate hydrogen gas and hydroxide ions. Chlorine gas further reacts with water to form chlorine - based substances such as hypochlorous acid and hydrochloric acid, which play a role in sterilization and disinfection. Chlory's seawater electrolysis technology has achieved remarkable results in nuclear power plant applications.
2. Advantages of Seawater Electrochlorination Technology
- Abundant raw materials and low cost: Seawater is an inexhaustible raw material. Compared with other chemical agent treatment methods, it can significantly reduce the cost of raw materials.
- Simple operation: The technology has a high degree of automation, which is easy to realize continuous operation and remote monitoring, reducing the complexity of manual operation.
- Good treatment effect: It can quickly and efficiently kill bacteria, algae and other microorganisms in water, ensure that the water quality of the cooling system meets the standards, and guarantee the safe and stable operation of equipment.
3. Application Background of Seawater Electrochlorination in Brazilian Nuclear Power Plants
Most nuclear power plants in Brazil are located in coastal areas. For example, Angra Nuclear Power Plant is located in Angra dos Reis, Rio de Janeiro state, with abundant seawater resources, which provides a natural advantage for the application of seawater electrochlorination technology.

The cooling system is an important part of a nuclear power plant. If a large number of microorganisms in the cooling water breed, they will form biofilms, leading to pipeline blockage, reduced heat transfer efficiency, and even equipment corrosion, which seriously affects the safe operation of the nuclear power plant. The seawater electrochlorination technology can effectively solve this problem and meet the high requirements of nuclear power plants for the water quality of the cooling system.
4. Specific Application Example of Seawater Electrochlorination in Brazilian Nuclear Power Plants - Taking Angra Nuclear Power Plant as an Example
4.1 Application Links
The cooling system of Angra Nuclear Power Plant is the main application place of seawater electrochlorination technology. In the circulating water link of the cooling system, after seawater is introduced, it first undergoes pretreatment to remove large impurities, and then enters the electrolytic device for seawater electrochlorination treatment. The treated seawater enters the cooling system to cool equipment such as nuclear reactors, and then is discharged back to the sea.
In addition, seawater electrochlorination technology also plays an important role in the pretreatment link of the circulating water system, which can reduce the pollution of pretreatment equipment by microorganisms in water.
4.2 Application Effects
By applying seawater electrochlorination technology, the microorganisms in the cooling system of Angra Nuclear Power Plant have been effectively controlled, the formation of biofilms has been significantly inhibited, the heat transfer efficiency of the cooling system has been improved, and the normal operation of equipment has been guaranteed.
At the same time, this technology has reduced equipment corrosion caused by microbial growth, reduced the maintenance cost and replacement frequency of equipment, and prolonged the service life of equipment. According to relevant data, after the application of seawater electrochlorination technology, the maintenance cost of the cooling system of Angra Nuclear Power Plant has been reduced by approximately 20%.
5. Challenges and Solutions in the Application of Seawater Electrochlorination in Brazilian Nuclear Power Plants
5.1 Challenges Faced
- The salinity and temperature of seawater fluctuate greatly, which will affect the electrolysis efficiency. In some coastal areas of Brazil, the salinity and temperature of seawater change significantly with seasons. When the salinity is too low or too high and the temperature is not appropriate, the electrolytic device is difficult to achieve the best electrolysis effect, which affects the production of chlorine - based substances.
- The generated chlorine - based substances may have a certain impact on the marine environment. Although chlorine - based substances will gradually decompose after playing their role in the cooling system, some residual substances still enter the sea with the discharged water, which may have an adverse impact on the living environment of marine organisms.
5.2 Solutions
- In view of the problem of fluctuations in seawater salinity and temperature, an intelligent control system can be adopted. By real - time monitoring parameters such as seawater salinity and temperature, the operating parameters such as current and voltage of the electrolytic device can be automatically adjusted to adapt to changes in seawater conditions and ensure the stability of electrolysis efficiency.
- To reduce the impact on the marine environment, the discharged water can be further treated. For example, dechlorination technology is used to reduce the content of chlorine - based substances in the discharged water to meet the environmental protection discharge standards. At the same time, strengthen the monitoring of the marine environment, timely grasp the impact of discharged water on the marine ecology, so as to take corresponding countermeasures.
6. Future Outlook
With Brazil's emphasis and development on nuclear power energy, more nuclear power plants may be built in the future. Chlory has been committed to the development and research of seawater electrolysis technology. As an efficient, economical and environmentally friendly water treatment technology, seawater electrochlorination technology is expected to be more widely used in newly built nuclear power plants around the world.

At the same time, with the continuous innovation and progress of technology, seawater electrochlorination technology will make greater breakthroughs in improving electrolysis efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and reducing environmental impact. For example, developing new electrode materials to improve the service life and electrolysis efficiency of electrolytic devices; optimizing the electrolysis process to reduce operating costs, etc.
In addition, combining with other water treatment technologies, such as membrane separation technology, can further improve the effect and water quality of water treatment in nuclear power plants, and provide more reliable guarantee for the safe and stable operation of nuclear power plants.
